Medical Study About The Mixture CA-L12 About Cancer Treatment

VISCUM ALBUM PLANT:
The mistletoe lectins in the herb are hypotensive,anti cytotoxic , and immune – stimulating . It causes improvement symptoms of chronic joint conditions, and significant lengthening of several times of cancer patients as well an improvement of quality of life.
Indications and usage:
The stem of the herb is used for its calming effect: in the treatment of mental and exhaustation: and as tranquilizer against nervous conditions such as agitation, anxiety, and increase excitability.
Approved by commission E:
TUMOR THERAPY
RHEUMATAISM
It is used for treating degenerative inflammation of joints and as palliative therapy for malignant tumors through non specific stimulation. Other uses include long term therapy for cases of mild high pressure and as atherosclerosis prophylactic.
It also may used for high blood pressure , epilepsy , whooping cough , asthma , vertiginous attack , amenorrhea , diarrhea , chorea , nervous tachycardia and hysteria .
The herb is used for joint pain, tendon and muscle pain, lumbago, back pain, vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and a Galatia.
Contraindications:
Protein oversensitivity, chronic progressive infections e.g., tuberculosis, and conditions of high fever
Precautions and adverse reactions:
No health hazards or side effects are known in conjunction with the proper administration of designated therapeutic dosages. The berries are said to have emetic and evacuant effects and to have caused the death of children. However unambiguous proof for these effects does not exist.
The wheal formation and the elevation of body temperature are considered as signs of immune system stimulation and therefore as positive therapeutic effects.
Daily dosage:
The recommended dose daily dosage is 10 gm
The dosage foe medicinal tea is 1 to 2 cups daily, EUROPEAN MISLETOE WINE dosage is 3 to 4 glasses daily.
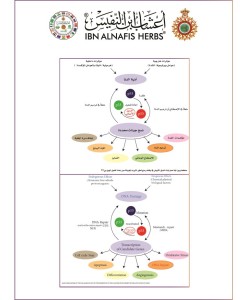
The mechanism of the viscum album plant action as anti cancer by the reactivation of the inactivated p53 gene but what that means the researchers has approved that the gene p 53 which is located on the shot arm of the chromosome no: 17 it is an inhibitor gene for tumor growth and it is doing its role as anti malignant tumors through a lot of many mechanism play a role in apoptosis, genomic stability, and inhibition of angiogenesis through several mechanism:
1-It can activate DNA repair proteins when DNA has sustained damage.
2- It can induce growth arrest by holding the cell cycle at the G/S regulation point on DNA damage recognition (if 3- it holds the cell for long enough , the DNA repair proteins will have time to fix the damage and the cell will be allowed to continue the cell cycle).
4- It can initiate apoptosis, the programmed cell death, if DNA proves to be irreparable.
When the human body exposed to hypoxia or stress injury the human body is going to activate the p 53 gene to stop the cell grow thing in the g1/s phase that give the time to proteins to repair DNA so it doesn’t permit it to pass into the next stage of the cell division stages.
If there is a mutation of one of the two inherited genes the persons will susceptible to cancer occurrence an usually it develops in the two life peaks and the mutation in these genes was found in most viewed malignant tumors.
الجرعة اليومية THE DAILY DOSAGE
10 ملغ مرة إلى مرتين يوميا وبجرعة عظمى 3 – 4 مرات في اليوم.10 MG one to two times daily and from 3 -4 times daily as a maximum dosage
The viscm album plant fights cancers and tumors by inhibiting the growth of cancer and by stimulating a host mediated response. NATURAL KILLER cells are also promoted enhance the immune system .It is often used in conjunction with chemotherapy to increase cancer survival rates. The viscm album plant fights is being proposed as an inhibitor of HIV replication based on in vitro study.
The viscm album plant fights has also demonstrated itself to activate interferon production .VISCUM ALBUM PLANT has also been found to regenerate damaged bone marrow, increase energy levels and offer pain relief in cancer patients
URTICA DIOCIA:
The root has been shown to cause an increase in the volume of urine, increase of maximum urinary flow, and reduction of residual urine. One study found that an aqueous extract of the root was the effective in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia. The extract inhibited the binding of the sex hormone –binding globulin (SHBG) TO its receptors on the human prostatic membranes in a dose related manner. Inhibition was noted as at 10 mg/ml
PAGE NUMBER 729 IN THE PRD FOR HERBAL MEDICINE. No health hazards or side effects are known in conjunction with the proper administration of designated therapeutic dosages FOR CHILDERN (OVER 4 MONTHS) AND ADULTS.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE APPROVED BY COMMISSION E:
INFECTIONS OF THE LOWER AND UPPER URINARY TRACT
INFECTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY TRACT
INFECTIONS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
KIDNEY AND BLADDER STONES
RHEUMATISM
And this list of the tumors can be treated by the mixture:
Acoustic Neuroma
Astrocytoma:
Grade I – Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Grade II – Low-grade Astrocytoma
Grade III – Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Grade IV – Glioblastoma (GBM)
Chordoma
CNS Lymphoma
Craniopharyngioma
Brain Stem Glioma
Ependymoma
Mixed Glioma
Optic Nerve Glioma
Subependymoma
Medulloblastoma
Meningioma
Metastatic Brain Tumors
Oligodendroglioma
Pituitary Tumors
Primitive Neuroectodermal (PNET)
Other Brain-Related Conditions
Schwannoma
Craniopharyngioma
Ependymoma
Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma (JPA)
Medulloblastoma
Optic Nerve Glioma
Pineal Tumor
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET)
Rhabdoid Tumor
And is a list of the urogenital tumors can be treated by the mixture:
Bladder cancer (especially transitional cell carcinoma)
Prostatic cancer (especially adenocarcino)
Kidney cancer (especially adenocarcinoma and in less effective on squamous cell carcinoma)
Testicular tumors especially these types:
Germ cell tumors
Seminomas
Non seminoma:
Embryonal carcinoma
Yolk sac carcinomas
Choriocarcinomas
Teratomas
Ovary tumors (especially epithelial ovarian tumors and germ cell tumors)
REFERENCES
AGRAWAL, V. and SARDAR, P.R. In vitro propagation
of Cassia angustifolia through leaflet and cotyledon
derived calli. Biologia Plantarum, March 2006, vol. 50, no.
1, p. 118-122.
ARAI, M.; SAITO, T.; KANEKO, Y. and MATSUSHIMA,
- Cellular origin and ultrastructural changes of
regenerating shoots from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Beegum, A.S. et al.
121
internodes cultured in vitro. Physiologia Plantarum, April
1997, vol. 99, no. 4, p. 523-528.
BECKER, Y. and OLSHEVSKY, U. Inhibition of herpes
simplex virus replication by camptothecin. Israel Journal of
Medical Sciences, 1973, vol. 9, no. 11-12, p. 1578-1581.
BODLEY, Annette L.; CUMMING, Jared N. and
SHAPIRO, Theresa A. Effects of camptothecin, a
topoisomerase I inhibitor, on Plasmodium falciparum.
Biochemical Pharmacology, March 1998, vol. 55, no. 5, p.
709-711.
CREEMERS-MOLENAAR, J.; HAKKERT, J.C.; VAN
STAVEREN, M.J. and GILISSEN, L.J.W. Histology of the
morphogenetic response in thin cell layer explants from
vegetative tobacco plants. Annals of Botany, May 1994,
vol. 73, no. 5, p. 547-555.
DE PAIVA NETO, Vespasiano Borges; DA MOTA, Tiago
Ribeiro and OTONI, Wagner Campos. Direct
organogenesis from hypocotyl-derived explants of annatto
(Bixa orellana). Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture,
November 2003, vol. 75, no. 2, p. 159-167.
DENNIS, Thomas T. and BOBAN, Philip. Thidiazuroninduced high-frequency shoot organogenesis from leafderived callus of a medicinal climber, Tylophora indica
(Furm. f.) Merrill. In Vitro Cellular and Development
Biology – Plant, March-April 2005, vol. 41, no. 2, p. 124-
128.
DHAR, Uppeandra and JOSHI, Mitali. Efficient plant
regeneration protocol through callus for Saussurea
obvallata (DC.) Edgew. (Asteraceae): effect of explant
type, age and plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Reports,
June 2005, vol. 24, no. 4, p. 195-200.
FAISAL, M. and ANIS, M. An efficient in vitro method for
mass propagation of Tylophora indica. Biologia Plantarum,
June 2005, vol. 49, no. 2, p. 257-260.
GIOVANELLA, B.C.; STEHLIN, J.S.; WALL, M.E.;
WANI, M.C.; NICHOLAS, A.W.; LIU, L.F.; SILBER, R.
and POTMESIL, M. DNA topoisomerase I-targeted
chemotherapy of human colon cancer in xenografts.
Science, November 1989, vol. 246, no. 4933, p. 1046-1048.
JAPAN PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
CENTER. Drugs in Japan, Ethical Drugs. Yakugyo Jiho
Co.; Tokyo, 1995, 169-270 p.
JOSE, B. and SATHEESHKUMAR, K. In vitro mass
multiplication of Ophiorrhiza mungo Linn. Indian Journal
of Experimental Biology, June 2004, vol. 42, no. 6, p. 639-
642.
KAWIAK, Anna; KROLICKA, Aleksandra and
LOJKOWSKA, Ewa. Direct regeneration of Drosera from
leaf explants and shoot tips. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ
Culture, November 2003, vol. 75, no. 2, p. 175-178.
KIRTIKAR, K.R. and BASU, B.D. Indian Medicinal
Plants Vol. II. 2
nd
- M/S Bishen Singh Mahendrapal
Singh, New Delhi, India, 1975. p. 1268-1269.
KNOLL, K.A.; SHORT, K.C.; CURTIS, I.S.; POWER,
J.B. and DAVEY, M.R. Shoot regeneration from cultured
root explants of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.): a system
for Agrobacterium transformation. Plant Cell Reports,
December 1997, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 96-101.
LIAO, Zhihua; CHEN, Min; TAN, Feng; SUN, Xiaofen